·
Energy Stores and Systems
The eight stores of energy:
- Thermal Energy
- Kinetic Energy
- Gravitational Potential Energy
- Elastic Potential Energy
- Chemical Energy
- Magnetic Energy
- Electrostatic Energy
- Nuclear Energy
Equations

These equations are extremely useful in I/GCSE Physics exam!👨🏫
Specific Heat Capacity
The specific heat capacity of a substance is the amount of energy required to raise the temperature of one kilogram of the substance by one degree Celsius.
Power
Power is defined as the rate at which energy is transferred or the rate at which work is done.

Conservation and dissipation of energy
Energy transfers
Energy can be transferred through heat or by doing work. For example:
- The initial force exerted by a person to throw a ball upwards does work. It causes an energy transfer from the chemical energy store of the person’s arm to the kinetic energy store of the ball and arm.
- A ball dropped from a height is accelerated by gravity. The gravitational force does work. It causes energy to be transferred from the ball’s gravitational potential energy store to its kinetic energy store.
- The friction between a car’s brakes and its wheels does work as it slows down. It causes an energy transfer from the wheels’ kinetic energy stores to the thermal energy store of the surroundings.
- In a collision between a car and a stationary object, the normal contact force between the car and the object does work. It causes energy to be transferred from the car’s kinetic energy store to other energy stores, e.g. the elastic potential and thermal energy stores of the object and the car body.
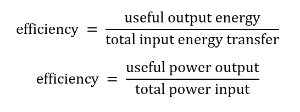
Efficiency
Reference:
https://getrevising.co.uk/resources/energy3
This is the end of the topic!

Drafted by Cherry (Chemistry)

