In A2/A-Level Mathematics, we will discuss non-uniform acceleration.
Theory
In A2/A-Level Mathematics, Consider a particle P moving in a straight line from a starting point O.
The displacement from O is x at time t . The initial conditions are: t ≥ 0 when x=0. if v is the velocity of P at time t, then
v = dx/dt
The acceleration 'a' of particle P is defined as:
a = dv/dt =d2x/dt2
or alternately,
a = dv/dt
= (dv/dt)(dx/dt)
BUT v = dx/dt
a = v(dv/dx)
In A2/A-Level Mathematics, Problems on this topic are solved by analysing the information given to form a differential equation. This is then integrated, usually between limits.
Example #1
A particle moves in a straight line such that its acceleration 'a' at time 't' is given by:
a = 4t-7
If the initial speed of the particle is 5 ms-1, at what values of 't' is the particle stationary?
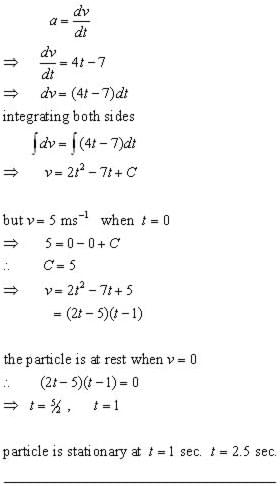
Example #2
A particle moves from a point O in a straight line with initial velocity 4 ms-1.
if v is the velocity at any instant, the acceleration a of the particle is given by:
a = 3/v
The particle passes through a point X with velocity 8 ms-1.
i) how long does the particle take to reach point X?
ii) what is the distance OX?(1 d.p.)
i)
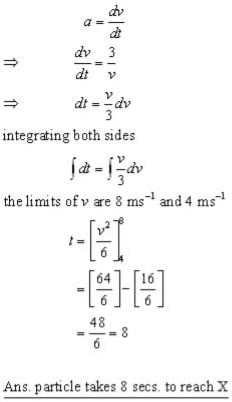
ii)
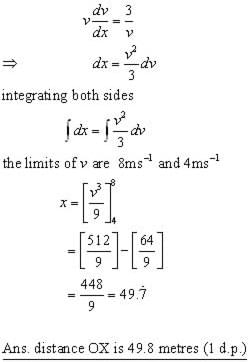
That's the end of the topic in A2/A-Level Mathematics.

