Breathing
Usually in IGCSE biology curriculum, cellular respiration is the process that releases energy from food in your cells. Our cells need a constant supply of oxygen for this to occur aerobically. Your respiratory system is an organ system adapted to allow the exchange of oxygen and carbon dioxide. Your bring are into the body through the mouth and nose. On the way in, the air is made warm and moist and any dirt or pathogens are filtered out of it by the cilia and mucus. The lungs are organs where gas exchange takes place.
Structure Of The Human Gas Exchange System
There are some highlights of structures in the IGCSE biology, they are:
- Nasal passages - warm, clean and add moisture to the air.
- Epiglottis - stops food getting into lungs when you swallow
- Oesophagus - carried food to the stomach
- Larynx - voice box
- Trachea - this is a tube with incomplete rings of cartilage which carries air to lungs. It is lined with cells that make mucus and cilia which moves the mucus away from the lungs.
- Left bronchus - carries air to lungs
- Bronchioles - carry air to the lungs
- Alveoli - tind air sacks adapted for gaseous exchange, with a large surface area.
- Diaphragm - sheet of muscle with fibrous part in the middle which is domed. It helps to make breathing movements and separates the thorax from the abdomen
- Ribs - bones that protect and ventilate lungs
- Internal intercostal muscles - pulls ribs down and in when you breathe
- External intercostal muscles - pulls ribs up and out when you breathe
- Pleural membranes - thin moist membranes which form an airtight seal around lungs and separates inside of thorax from lungs
- Pleural fluid - liquid which fills pleaural cavities and acts as lubrication so that the surfaces of the lungs do not stick to the inside of the chest wall
Ventilating Lungs
Air is moved into and out of the lungs by movements from the diaphragm and ribs. Ventilation brings in oxygen-rich air and removes carbon dioxide. It maintains diffusion gradients in the alveoli. There is always more oxygen and less carbon dioxide in the air in the lungs than in the blood. The ventilation movements of the ribs and diaphragm changes the volume and pressure of the chest cavity.
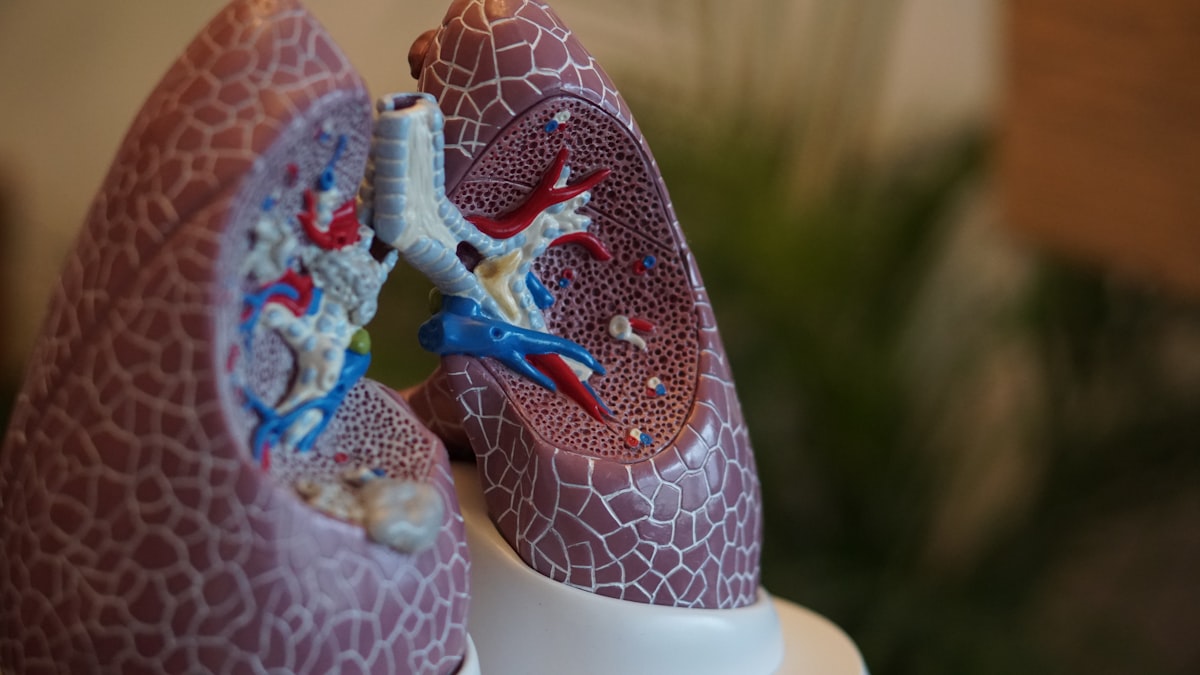
Gas Exchange In The Alveoli
The lungs contain millions of tiny air acs called alveoli which are adapted for efficient gas exchange. Blood is pumped from the heart to the lungs and passes through the capillaries surrounding the alveoli. Carbon dioxide diffuses from the blood into the air in the alveoli. Oxygen diffuses from the air in the lungs into the blood. The oxygenated blood travels back to the heart to be pumped around the body.
There are 3 ideas of alveoli that need to remember in IGCSE biology, alveoli have:
- a large surface area
- short diffusion distance between the air and the blood
- a rich blood supply which removes oxygen and delivers carbon dioxide to the air.
Smoking and Health
In IGCSE Biology curriculum, tobacco has many effects on smokers:
- Cilia gets destroyed and therefore dirt and bacteria are unable to be removed
- Emphysema - walls of the alveoli are damaged and break down to form large irregular air spaces which do not exchange gases efficiently.
- Lung cancer - tar and other chemicals cause cells to mutate and form cancers in the lungs and throat.
- Carbon monoxide binds to hemoglobin in the blood which lowers oxygen levels in the blood. In pregnant women, the fetus gets deprived of oxygen.
- Increases the risk of heart attacks and strokes

The end of part I ! (remember to read part II)

Drafted by Gina (Biology)

