In this topic of IBDP Mathematics, we will be learning about different ways to solve quadratic equations.
Factoring Quadratic Equations
- If xy=0, then x=0 or y=0.
- This is known as the zero product property.
- This property can be expanded to:
- If (x - m)(x - n)=0, then either x - m=0 or x - n=0
In IBDP Mathematics, the zero product property can be used to solve for quadratic equations - this method is known as factoring.
If the quadratic equation is given in the form of (x - m)(x - n)=0, then, by the zero product rule, either x - m=0 or x - n=0.
- Given that there are these possibilities, then to solve for all the possible values of x, one must solve both x - m=0 and x - n=0.
- Thus, the values of x are m and n.
- For example:
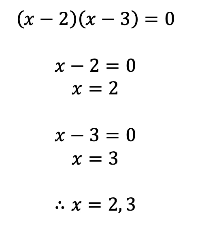
If the quadratic equation is given in the form of ax2+bx+c = 0, with a=1, and b and c being integers, then you will need to factorise the equation in order to get it in the form of (x - m)(x - n)=0.
- In order to do this, you will need to find two numbers, where the sum of those numbers is equal to b, and the product of those numbers is equal to c.
- Those two numbers will become m and n respectively.
- i.e. m + n=b, m x n=c.
- Once you have found those two numbers, you can rewrite the equation in the form (x - m)(x - n)=0, and solve using the method above.
- In order to check your work, you can expand the brackets to see if you arrive at the intial equation.
- For example:
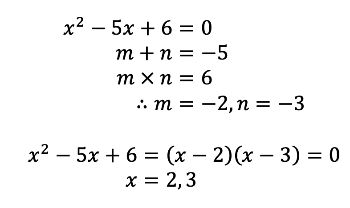
If the coefficient of x2 (i.e. a) does not equal 1, but a,b and c share a common factor, factor out the common factor and solve as above.
- For example:
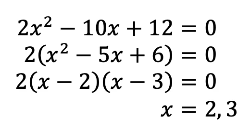
If the coefficient of x2 (i.e. a) does not equal 1, and a,b,c don't share a common factor, then one can attempt to compute the equation by factoring the equation as follows.
- Find two numbers (m and n) that multiply to give ac (i.e. a x c) and add to give b.
- i.e. m x n = a x c, and m + n = b
- Rewrite the middle part of the equation (i.e. bx) using m and n.
- i.e. ax2 + bx + c = ax2 + mx + nx + c = 0
- Factor out the common factor of the first two terms and the last two terms separately.
- If the step above is done correctly, then one should have a clear common factor.
- Factor out the common factor, and solve as above.
- For example:
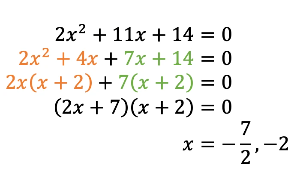
The Quadratic Formula
Another way to solve quadratic equations is by using the quadratic formula. In IBDP Mathematics, the quadratic formula is given in the formula booklet.
- The quadratic formula is a way to solve all quadratic equations. Given that not all quadratic equations can be factorized, then having the quadratic formula on hand can be useful.
- The quadratic formula is given below:
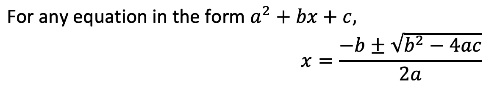
To use the quadratic formula, simply substitute the values of the coefficients (i.e. a, b and c) into the formula to solve for all the possible values of x. For example:
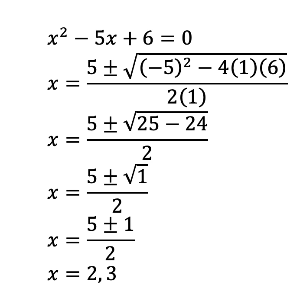
Completing the Square
One final method of solving quadratic equations in IBDP Mathematics is completing the square.
- Before using this method to solve quadratic equations, one must ensure that a=1 (i.e. the coefficient of x2 is 1). If a does not equal 1, then divide the whole equation through by 1/a.
- First, subtract both sides of the equation by c. This leaves you with ax2+bx = -c
- Divide b by 2, square it, and add it to both sides of the equation.
- i.e. Add (b/2)2 to both sides of the equation.
- This creates a perfect square trinomial on the left side of the equation. This means you are able to rewrite the left side of the equation in the form (x + (b/2))2.
- Now, you are able to square root both sides, and solve for x.
- For example:
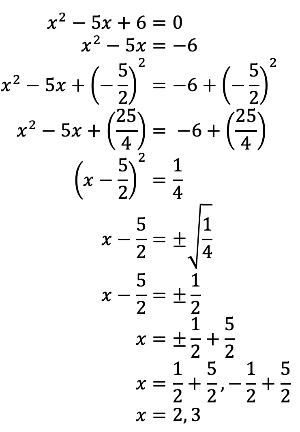
This is the end of this topic


