When it comes to A2/A-level Physics, do you remember simple harmonic motion?
Simple Harmonic Motion
- An object that oscillates freely about an equilibrium position is said to be undergoing simple harmonic motion.
- E.g. a pendulum or mass on a spring
- Simple harmonic motion can be used to determine information about the bodies:
(1) Displacement
(2) Velocity
(3) Acceleration
Displacement
- The x displacement of an object undergoing simple harmonic motion is the same as the x displacement of an object undergoing circular motion with the same period.
- rcosθ=x
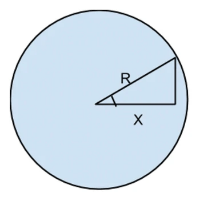
- θ can be replaced by wt because w= how much of a circle in 1 second.
- rcos(wt)=x
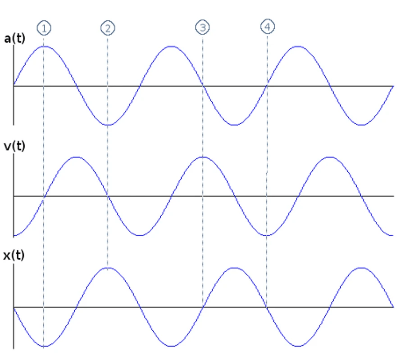
1- acceleration= max, velocity=0, displacement=min
2-acceleration=min, velocity= 0, displacement=max
3-acceleration=0,velocity=max, displacement=0
4- acceleration=0, velocity=minimum, displacement=0
Acceleration and displacement are equal but in opposite directions.
Velocity is the odd one out - it is ½ way between the two.
The restoring force is proportional to displacement but in the opposite direction.
- Velocitymax = Aw
- Velocity = -Awsin(wt)
- Accelerationmax = w2A
- Acceleration = -w2r
- Acceleration = -w2Acos(wt)
The Energy of a Spring Undergoing Simple Harmonic Motion
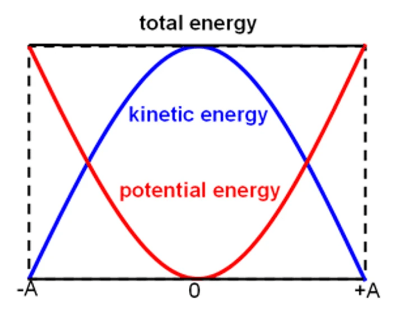
- This is assuming there are no forces working against it such as gravity and air resistance.
- To calculate the maximum potential energy E=1/2KX2, remember that x will be A at maximum x.
- Energy=½ k(acos(wt))2
- For kinetic energy =½ mv(-Awsin(wt))2
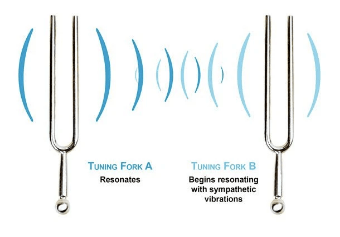
Resonance
- If a system is undergoing simple harmonic motion and allowed to oscillate freely, it will oscillate at it’s natural frequency.
- A system can be made to oscillate by a periodic driving force.
- If the frequency of the periodic driving force is the same as the natural frequency of the system, large amplitude oscillations called resonance occur.
- Energy transfer between the system and the oscillation system is most efficient.
Damping
In reality oscillations are often damped meaning the amplitude gradually decreases as energy is dissipated as work done against friction of drag forces.
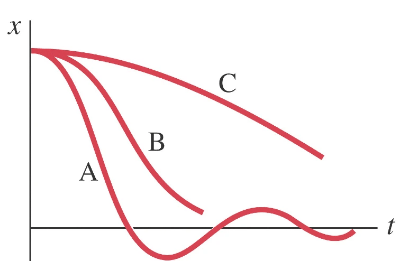
- A= light damping - Period stays the same but amplitude decreases steadily.
- B= Critical damping - stop the system from oscillating after being displaced = just returns to equilibrium.
- C= Overdamping- Where the system takes a long time to return to equilibrium.
That's the end of the topic!

Drafted by Bonnie (Physics)

